- Not having teeth can do more than just leave a hole in your smile. They can change the way you talk, lower your confidence, and even make it hard to enjoy your favourite foods. We know how personal this can be at Sparsh Dental Care.
- A dental bridge is a safe and effective way to restore both function and appearance without having to undergo surgery. It literally fills in the space in your mouth so you can smile again.
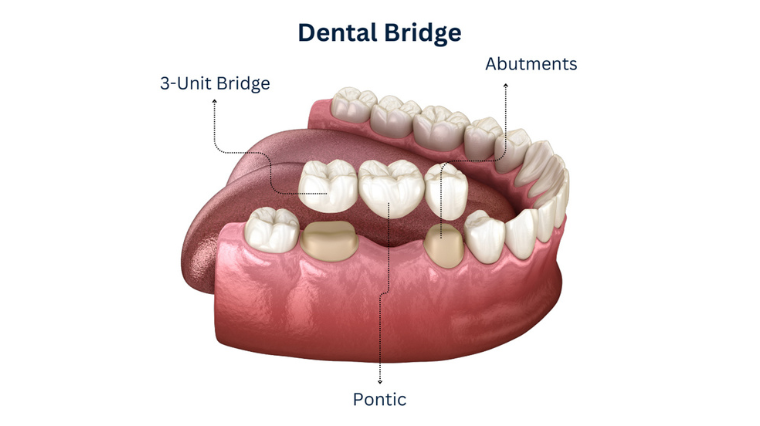
What Is a Dental Bridge?
- A dental bridge is a permanent way to replace one or more missing teeth. As the name suggests, it fills in the gap left by missing teeth with an artificial tooth called a pontic. This pontic is securely supported by the neighbouring natural teeth or dental implants, called abutments.
- A dental bridge restores both function and appearance once it is in place. It helps you speak clearly, chew properly, and smile without thinking.
Types of Dental Bridges: Which One is Right for You?
- Traditional dental bridge: Supported by crowns on both sides of the gap. Ideal when adjacent teeth are strong and healthy.
- Cantilever dental bridge: Anchored on one side only. Suitable when there is just one neighbouring tooth.
- Maryland dental bridge: Uses bonded metal or ceramic wings. Often preferred for front teeth due to lower bite pressure.
How Is a Dental Bridge Placed?
- Initial Consultation: We check your teeth, take X-rays and discuss the best bridge option for your case.
- Tooth Preparation: Adjacent teeth (abutments) are gently shaped to hold the bridge securely.
- Impressions: Accurate moulds are taken to ensure a precise fit.
- Temporary Bridge: A temporary bridge is placed while the permanent one is prepared.
- Final Placement: Once ready, we place the bridge, adjust it for comfort and fix it with dental cement.
Get in Touch with Us
- Sparsh Dental Care is here to help you, whether you’re still looking into your options or are ready to start. We will give you expert advice, put your needs first, and be gentle. We are happy to answer all of your questions and make you feel better.
- You can call us or stop by for a meeting. Let’s help you feel good about your smile again.




